Polygon Hardfork: Upcoming Changes & More

Polygon is undoubtedly the Biggest Layer2 platform for ethereum scaling. After the launch of its POS chain, Poligon gave its users the benefit of faster transactions with lower fees while interacting on ethereum. But now with an increasing number of decentralised applications being created every day with 207 million unique addresses and 2.3 billion processed transactions Polygon chain is continuing to grow and produce successful crypto projects like Uniswap, Aave etc.
In order to make building even more seamless, polygon has proposed to improve the performance of its PoS chain via a critical hard fork scheduled to take place on 17th Jan 2023.
Before we dive into the details, what is a hardfork?
A hardfork in crypto is an event where a Blockchain splits into two separate block chains running parallel to each other with different parameters, forming their base.
When a HardFork change is made, it is not backward compatible meaning that all users will have to upgrade their software in order to continue participating in the network. In this case the fork splits into two separate versions one that follows the new rules and one that follows the old rules.
For example the most recent hard work was done by bitcoin in 2017 which resulted in a split, creating bitcoin cash.
Polygon’s aim from the hard-fork V0.3.1HardFork
After a long heated series of debates and discussions and feedback from the community, polygon decided that the hard fork will aim towards
1. Reduce severity of spikes in gas costs due to increasing demand
2. Address chain reorgs to reduce time to finality of the transaction
Understanding The Upgrades & Their Impacts In Depth
Problem 1: The exponential gas-price hikes
Proposed Solution: Changing the value of the ‘BaseFeeDenominator’ from 8 to 16 to smooth out the increase or decrease in base fee of a block.
Results Expected: This is work towards flattening the growth curve of gas prices, though prices will still hike when there is increased traffic, the unusual spikes will be controlled.
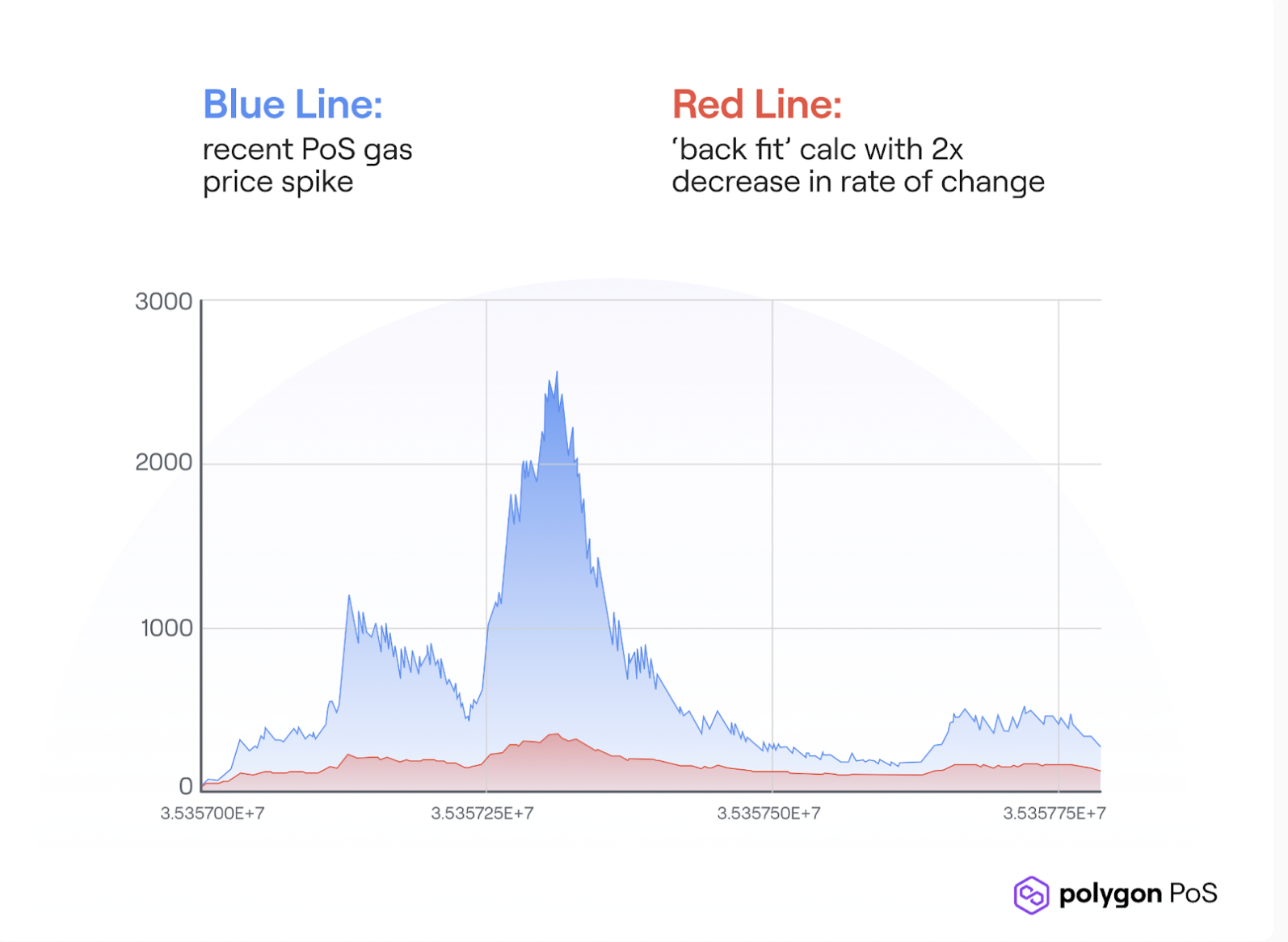
Problem 2: Addressing Chain Reorgs
To explain simply, a chain reorganisation abbreviated as a reorg occurs when a block is deleted from the block chain to make room for a longer chain.
A chain reorganisation can happen with busy blockchains like ethereum and bitcoin, where nodes may generate a new block simultaneously in the same place, if this happens, the note that produces the shorter chain deletes in order to allow the longer chain to rearrange.
This ensures that all new operators have the same copy of the distributed ledger.
Now, what problems do these reorgs cause?
Chain reorganisation often raises the risk of DeFi transactions failing, resulting in lower than expected trading returns and increased vulnerability of attacks.
Proposed Solution: Decrease the sprint length from 64 to 16 blocks. By reducing the length to 16 blocks, this upgrade means a single block producer will produce blocks continuously for a much shorter time decreasing the depth of reorgs.
“Sprint length” is described as the number of blocks a validator produces contiguous blocks on Bor chain. By reducing sprint length, the time a validator continuously produces blocks decreases.
Results Expected: By decreasing the sprint length, the hardfork will help reduce the frequency and depth of reorgs, and improve transaction finality.
In order to ensure a smooth transition for its users, Polygon has announced that all infrastructure providers will need to update their nodes before January 17th. The team has also emphasized that the hardfork will not affect the functioning of dApps on the network. Additionally, holders of MATIC and those who have delegated their tokens do not need to take any action in relation to the upcoming network changes.
You may have been left with a series of questions surrounding the Hard-Fork & your involvement as a user, developer or validator. All your questions have been answered by Polygon here: Read More
About ZeroSwap
ZeroSwap provides users a simplified way to swap on multichains with zero gas fees. We pay gas for users when they swap on-chain using meta-transactions.
We are live on Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Fantom, Optimism, CELO, Ethereum and Arbitrum.
In addition, our product suite includes the Gasless ZeroSwapDEX, Staking, IDO platform ZeeDO and our native Bi-directional Bridge, and a B2B Service Based Product called DeFi Wizard.
Join Us!
Website | Announcement Channel | Discord | Telegram | Twitter | Zeroswap Ecosystem | Reddit